Pretreatment
A variety of pretreatment procedures are employed at the Waikato Radiocarbon Dating Laboratory to ensure we date only material of secure chemical origins.

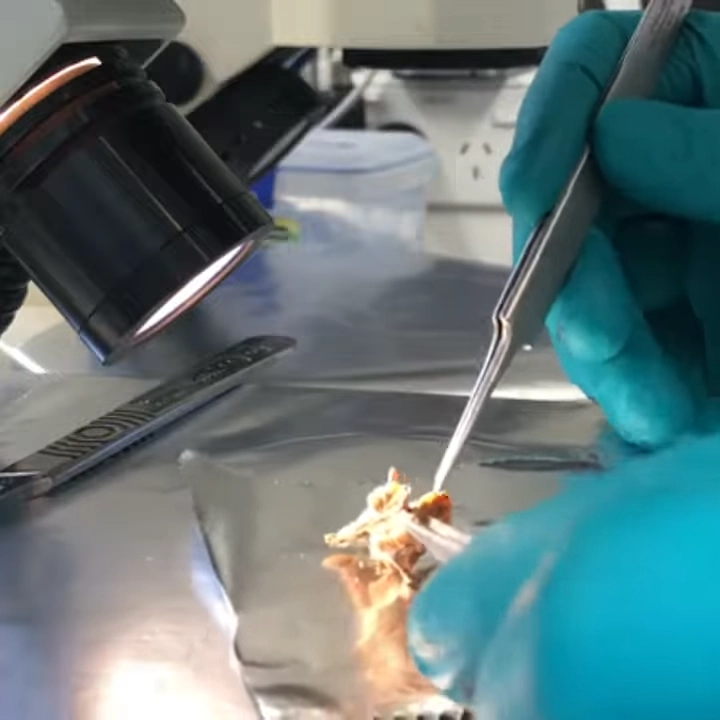
Sample inspection prior to chemical treatment.
We have listed the commonly dated sample types and potential problems. Take a look and if you require detailed information about a specific pretreatment method or have questions about a particular sample type, please contact us.
See our price list for optional pretreatment charges.
Inspection
All samples are closely inspected to isolate the most reliable fraction for dating. Often a sample may not be homogeneous, or there may be extraneous materials such as rootlets, thread, glue or some other visible contaminant in the sample. The sample is then washed in distilled water and crushed, or milled, to increase the surface area for subsequent pretreatment. Solvent extraction may be necessary to remove conservatives or glues.
Radiocarbon dating: Inspection and cleaning of a rat skull for 14C dating.
Inspection and cleaning of a rat skull for 14C dating. Lauren Linnenlucke (Phd candidate, James Cook University
Charcoal and Wood
These are pretreated using a dilute acid/dilute alkali/dilute acid treatment (commonly termed ABA). The chemical concentrations, temperature and length of pretreatment vary depending on the sample.
Please note: it may be necessary for the charcoal and wood to be identified to short lived species to avoid problems of inbuilt age. More information on inbuilt age can be found here.
For old wood samples (>20,000 BP), we recommend the cellulose fraction be extracted. The sample is treated with sodium chlorite to isolate holocellulose, rinsed, then treated with sodium hydroxide, and rinsed again (solvent extraction may be required depending on sample preservation). The sample is then washed with HCl, rinsed and dried. We will perform cellulose extraction and solvent extraction upon request at additional cost.
Bone

Glue and shellac contaminants on moa bone
Bone is acid washed in dilute HCl to isolate the bone protein, filtered, then gelatinised to remove contaminants. Gelatin designated for AMS dating is then ultrafiltered to further purify the gelatin.
Once the bone has been chemically treated, C and N isotopes are measured. This information provides important quality control indicators enabling the laboratory staff to assess if the bone preservation state is sufficient for reliable 14C analysis. This data also provides information on trophic level and 14C reservoir – both essential for date interpretation and calibration.
Please note: 15N and 13C values are included in the cost of bone pretreatment. We recommend contacting the lab before dating bone for the first time. All bone should be identified to species before dating.
Soil and Peat
Typically, the humin fraction is isolated from peat, soil and lake sediments using the ABA method. However, if requested we can isolate and date the total organic fraction or the humic fraction of the sample. The total organic fraction is isolated with a HCl wash which removes inorganic carbon and absorbed CO2, rinsed and dried. Humic acid is isolated by collecting the NaOH fitrate which is acidified with HCl to precipitate the humic fraction, then rinsed and dried.
Shells
Marine Shells
Marine shell samples are routinely etched with dilute HCl to minimise the possibility of contamination through isotopic exchange between the sample and its environment. All aragonitic shell samples are tested for recrystalisation prior to dating to ensure no chemical alteration has taken place. All shell should be identified to species before dating. More information on marine shell dating can be found here.
Freshwater/Terrestrial Shells
These undergo similar pretreatment to marine shell samples. Freshwater and terrestrial shells may obtain their carbon from a source (or reservoir) that is not well documented and may give results that are difficult to interpret. More information on reservoir effects can be found here.
Water
We date the dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) fraction of water which is separated using phosphoric acid following the method of Gao et al. (2014). The headspace gas is extracted and cryogenically purified before conversion to graphite powder for AMS analysis. Please contact the lab for instructions on collection and packaging.
Gao, P., X. Xu, L. Zhou, M.A. Pack, S. Griffin, G.M. Santos, J.R. Southon, K. Liu, 2014. Rapid sample preparation of dissolved inorganic carbon in natural waters using a headspace-extraction approach for radiocarbon analysis by accelerator mass spectrometry. Limnology and Oceanography: Methods 12:174-190.
Methane
Methane gas is converted to CO2 at 975°C and the CO2 is cryogenically collected and converted to graphite following the methodology of Pack et al. (2015). Please contact the lab for instructions on collection and packaging.
Pack, M.A., X. Xu, M. Lupascu, J.D. Kessler, C.I. Czimczik, 2015. A rapid method for preparing low volume CH4 and CO2 gas samples for 14C AMS analysis. Organic Geochemistry 78:89-98.
